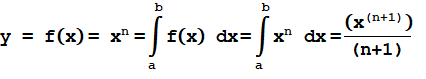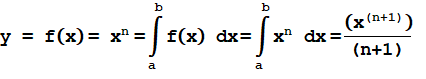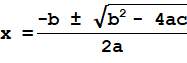Quadratic equation is given in the form: ax 2 + bx + c = 0, where ‘a’, ‘b’ and ‘c’ are constants and a ≠ 0. The solution to this quadratic equation is given by the following quadratic formula: Here b 2 – 4ac is called as discriminant. If b 2 – 4ac > 0, then the equation has two solutions. If b 2 – 4ac = 0, then the equation has one solution. If b 2 – 4ac < 0, then the equation has no real solutions. Using quadratic equation, it is possible to find the value of ‘x’, if ‘a’, ‘b’ and ‘c’ are known. For example, consider a 2 nd order polynomial equation: y = ax 2 + bx + c. By using quadratic formula, it is possible to determine the value of ‘x’ data when, y = 0. If y = 0, then 2 nd order polynomial equation becomes a quadratic equation as, 0 = ax 2 + bx + c when a ≠ 0. Example #1 In an experimental analysis, for a set of ‘x’ and ‘y’ data, the derived 2 nd order polynomial curve fit equation is: y = 2x 2 – 9x + 10. Determine t